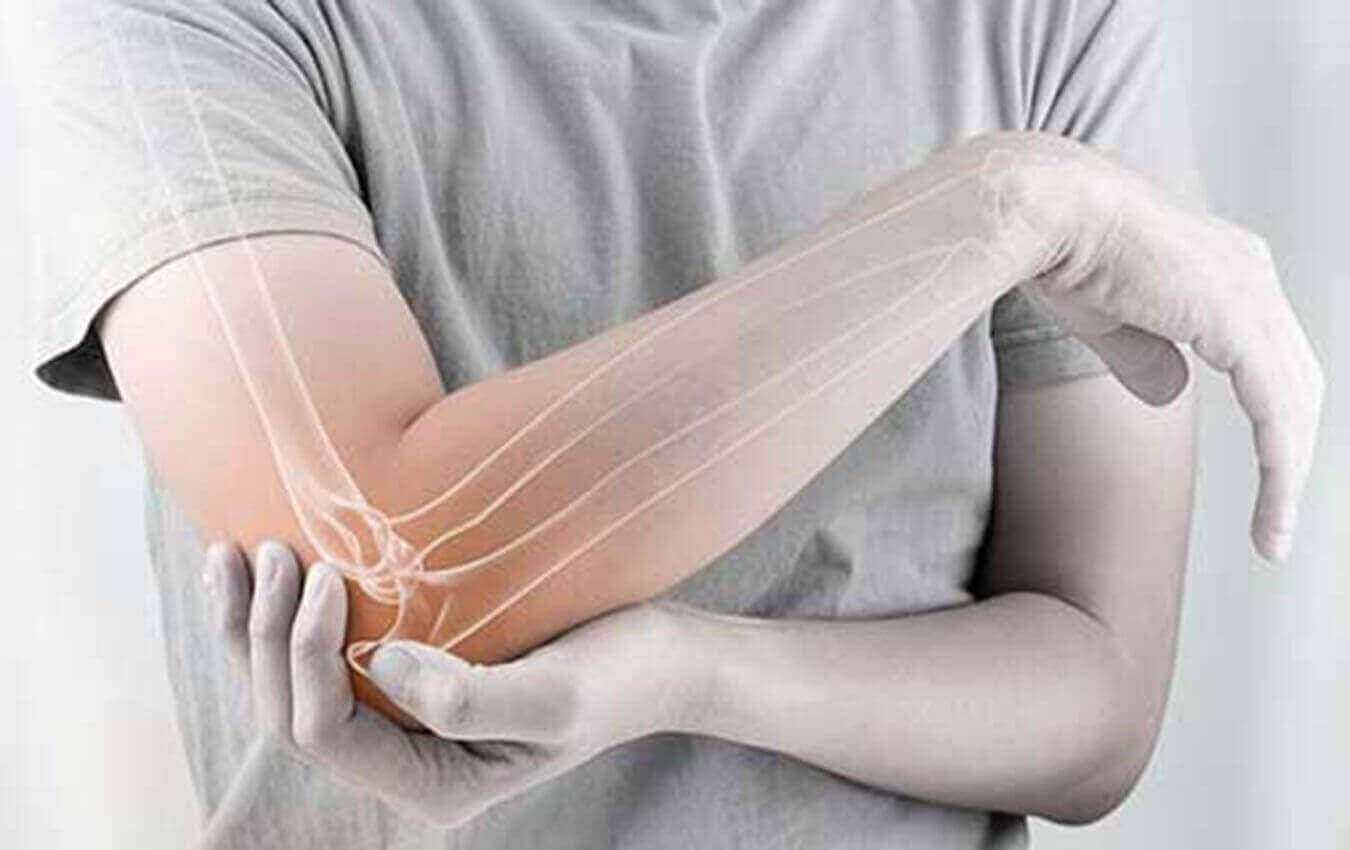
The elbow is a joint that comprises three bones; the humerus,
the radius, and the ulna. Your elbow joint flexes and
straightens like a hinge. Also, it is necessary to rotate the
forearm, that is, the capacity to turn your palm up or palm
down.
The elbow joins the upper arm, called the humerus, to the ulna and the radius, the bones that constitute the forearm. A fracture can arise in either one of the bones which form the elbow.
Rarely, an injury to the elbow might even move the bones of the joint out of place, limiting the rigidity and range of motion of the joint. This is termed a fracture-dislocation.
The elbow joins the upper arm, called the humerus, to the ulna and the radius, the bones that constitute the forearm. A fracture can arise in either one of the bones which form the elbow.
Rarely, an injury to the elbow might even move the bones of the joint out of place, limiting the rigidity and range of motion of the joint. This is termed a fracture-dislocation.
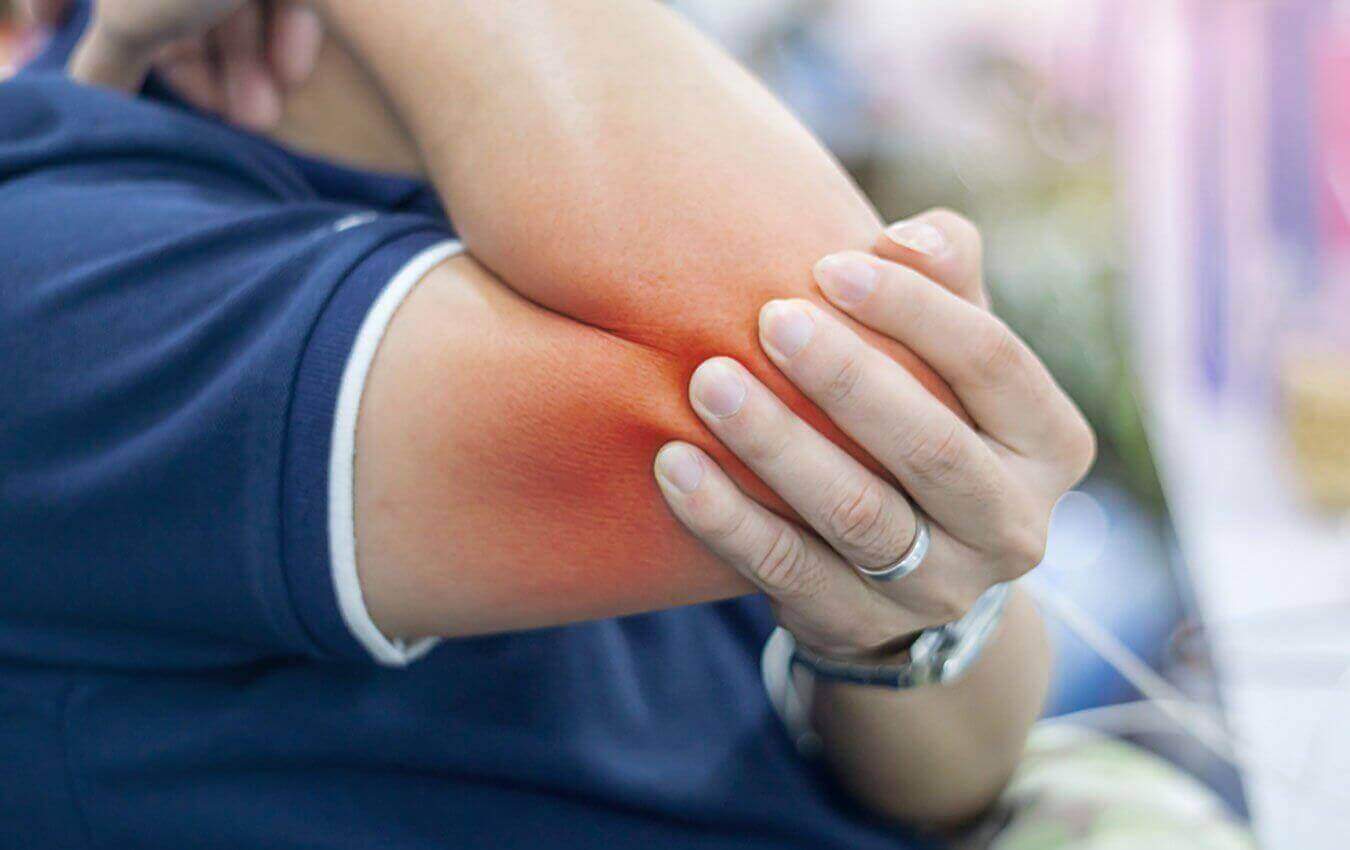
Fractures in the elbow cause various symptoms and
complications. They are:
- Prominent deformity visible at the elbow
- Inflammation and bruises on the elbow
- Immense pain in the elbow region or the whole arm
- Tightness in or around the elbow
- Possible numbness or weakness throughout the arms, wrists, and hands
- Crack or snap at the moment of the injury
Elbow fractures can occur from falling, a direct blow towards
the elbow, or twisting trauma to the arm. Sprains, strains, or
dislocations may develop at the very same time as a fracture.
The three most prevalent fractures that occur at the elbow
are:
- Distal humerus fracture: The distal humerus is the rounded bottom section of the bone linking the shoulder to the elbow. Distal humerus fractures happen due to a direct hit to the elbow, placing your hand out to prevent a fall, or landing on a bent elbow. Distal humerus fractures are relatively uncommon.
- lecranon fracture: Olecranon fractures generally happen only when tricep muscles over the elbow rapidly tense during a fall. The olecranon is the bone located at the point of the elbow. It is especially susceptible to fracture since muscles or any other tissues don't surround it.
- Radial head fracture: The radial head is just the bone in the elbow that joins with the humerus in the elbow joint. These fractures often occur when a person throws their arm out to prevent a fall. The impact can force the radial head to drive into the humerus so strongly that it creates a fracture.
Various risk factors induce elbow fractures:
- Falling into an outstretched arm, particularly from a standing posture, or a contorting injury to the arm.
- Elderly individuals are more prone to develop an elbow fracture.
- If you have osteoporosis or developing a condition that weakens the bones.
- Competing in sports like football, volleyball, wrestling, and gymnastics.
- Becoming post-menopausal or experiencing other diseases that result in bone or mineral loss.
Neurovascular injury results from damage to the vital blood
vessels serving the brain, brain stem, and higher spinal cord,
comprising the basilar, vertebral, and carotid arteries. Elbow
fractures can result in these injuries. Sometimes, the bones
broken protrude through the skin and makes the arm appear
misshapen.
If it occurs in an emergency department or during an office
visit, a physical exam of the damaged area is required to
diagnose an elbow fracture.
Further imaging might be required to confirm the occurrence and degree of the injury:
Further imaging might be required to confirm the occurrence and degree of the injury:
- A Computed Tomography scan or CT scan might be needed to provide a better detailed view of the fracture pieces.
- X-ray: A type of imaging used to determine whether or not fractures exist.
Non-surgical treatment: If the bones are correctly
aligned rather well, the doctor may recommend therapy in
plaster or brace for about a month. A follow-up x-ray one week
following the damage is usually required to ensure the bones
do not slip out of place.
Surgical treatment: If the bones do not fall in line, your doctor may propose resetting the bones to restore them in position. Often, this can be accomplished without surgery. More typically, pins, screws, or wires are necessary to hold the bones aligned for roughly a month while they recover. A plaster or cast is used chiefly for additional protection after surgery. Typically, the pins are short-term and will be removed after the bone is healed.
It takes about six weeks for the elbow fracture to heal completely, but you must keep moving your arm as this will speed your recovery.
Surgical treatment: If the bones do not fall in line, your doctor may propose resetting the bones to restore them in position. Often, this can be accomplished without surgery. More typically, pins, screws, or wires are necessary to hold the bones aligned for roughly a month while they recover. A plaster or cast is used chiefly for additional protection after surgery. Typically, the pins are short-term and will be removed after the bone is healed.
It takes about six weeks for the elbow fracture to heal completely, but you must keep moving your arm as this will speed your recovery.